Why use 3D CEll Culture?
In vivo, cells in tissues and tumors do not double every 2 – 4 days as they do in classical (2D) cell culture – so why use a technology developed in the 1950’s?
The CelVivo system creates an environment which promotes the growth and maintenance of large 3D tissue mimetic structures, whether they are spheroids, organoids, acini and other aggregates.
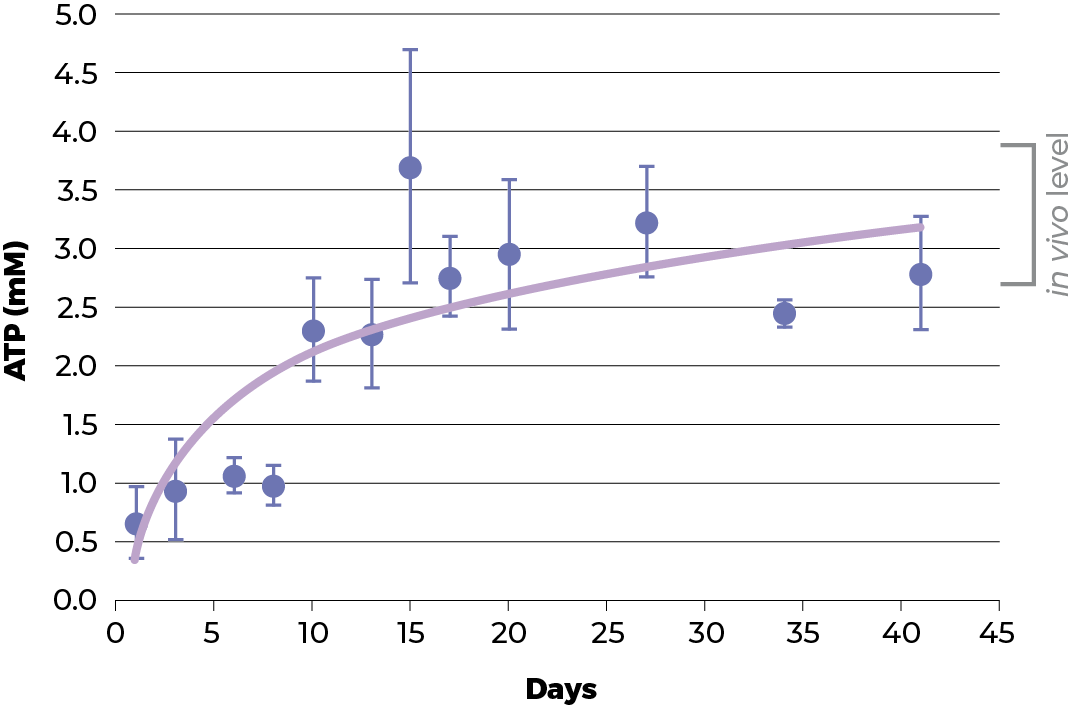
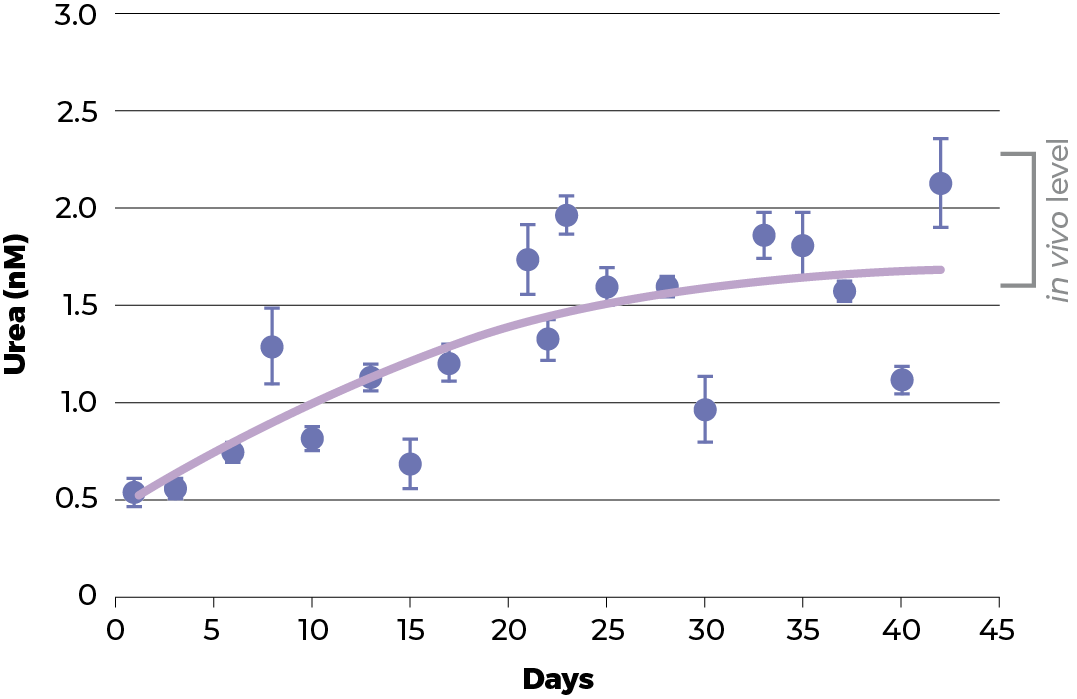
In this environment, liver spheroids remain in a stable dynamic equilibrium and exhibit human in vivo physiological performance for at least 24 days (i.e. up to at least 42 days of culture). During this time, the spheroids exhibit a stable transcriptome profile.
Reasons for Using 3D Cell Culture
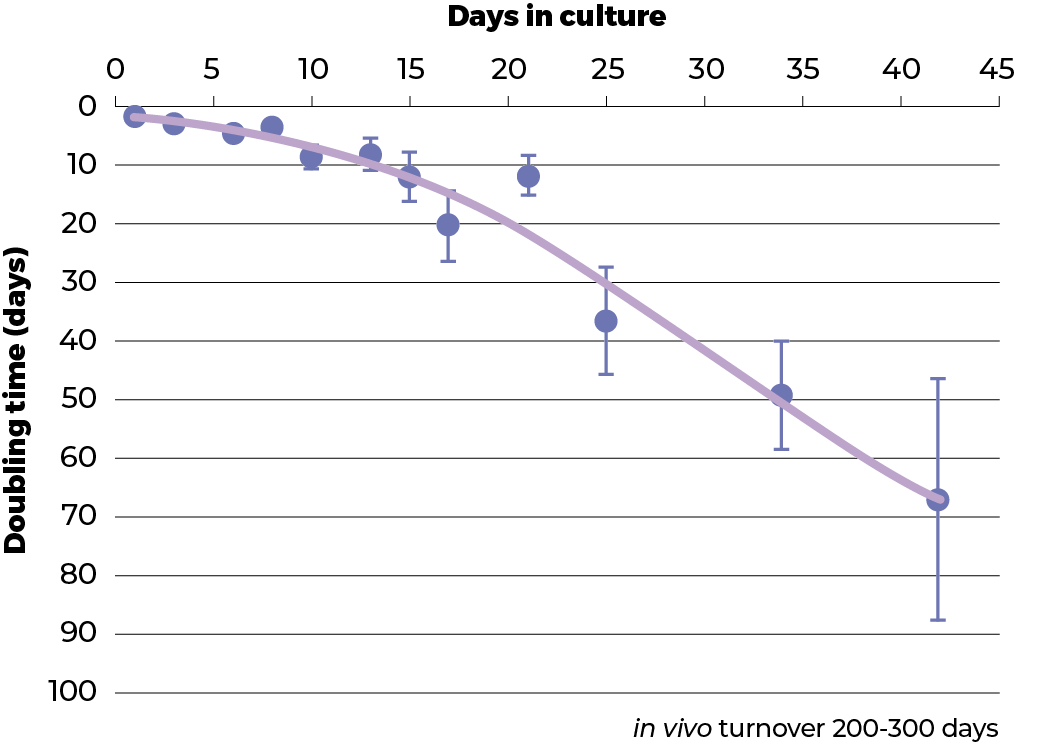
Proliferation
Slows from a doubling time of 1 day to 60 days after 40 days in culture. Resembles proliferation in the parental tissue or in tumours in vivo. Cultures can be maintained for over 300 days
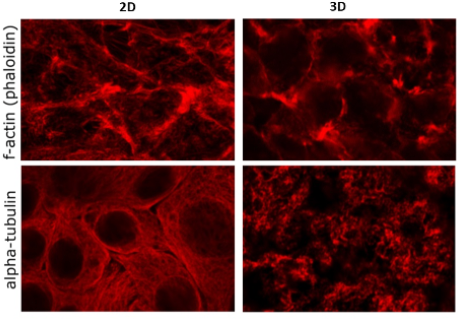
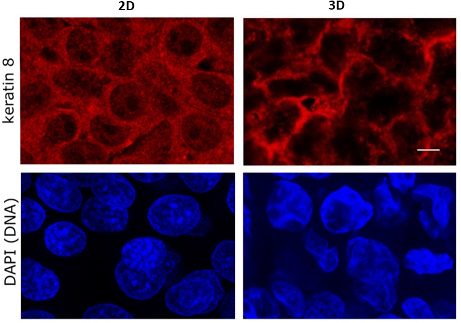
Architecture
Microfilaments (actin) microtubules (tubulin) and intermediate filaments (e.g. keratin) resemble that seen in vivo .
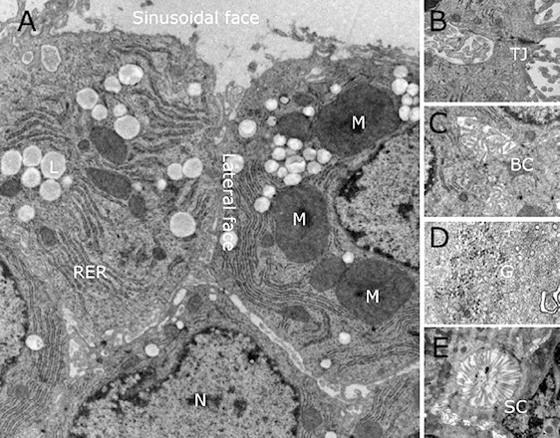
Ultrastructure
Resembles liver sections, showing plasma membrane differentiation, tight junctions, bile canaliculus-like channels, lipid droplets and glycogen granules.
Physiological performance
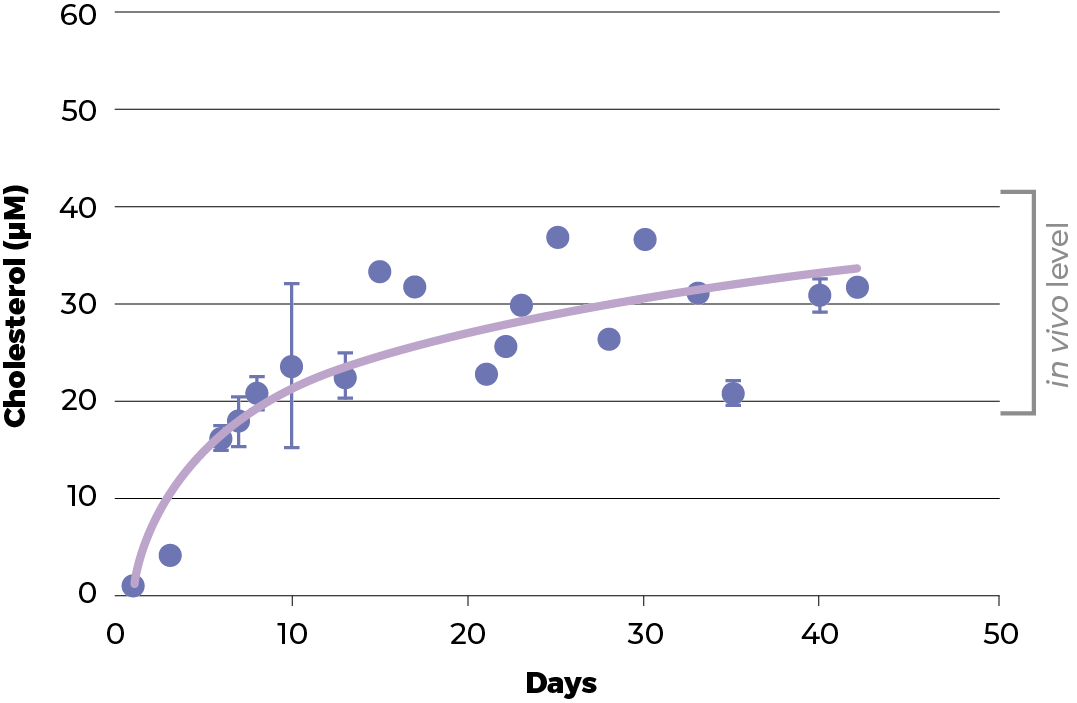
After 18 days of culture in ClinoStar the HEPG2 spheroids levels of ATP, urea and cholesterol reach levels seen in vivo. These results are compared to a regular 2D cell culture.
Cell viability was measured based on the spheroids ability to produce ATP. Urea production is increased after 5 days culture in 3D, in normal 2D cell culture the urea production is about 0.7 mM pr day. A similar trend was observed with cholesterol which also reach in vivo levels, when cultured in 3D.
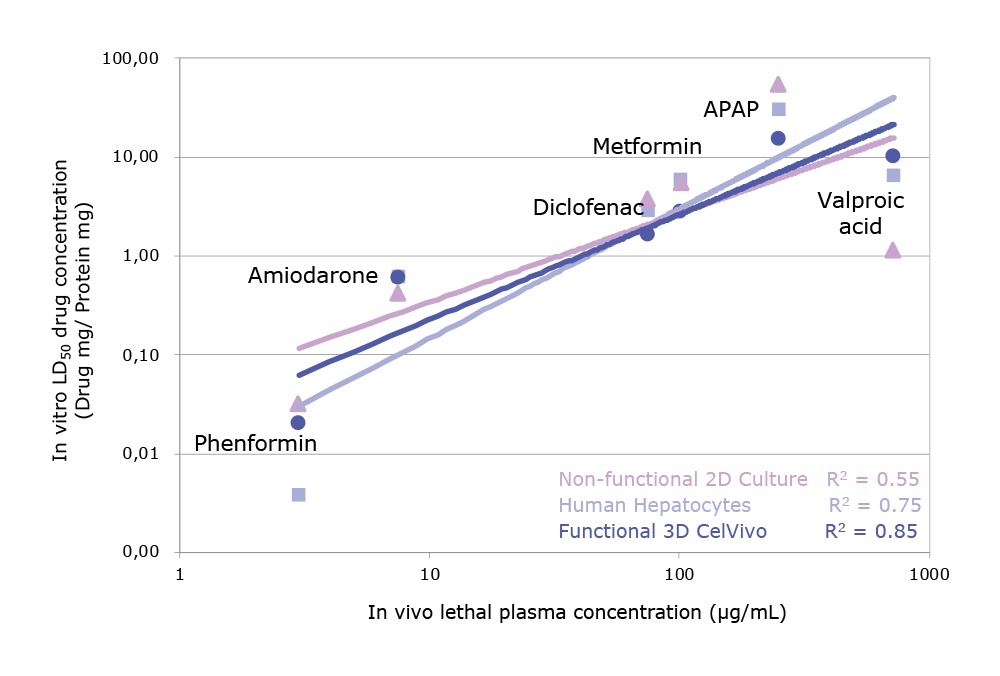
Drug metabolism
Toxicity measurements for Amiodorone, APAP, Metformin, Phenformin and Valproic acid are more accurate in 3D HEPG2 spheroids than those obtained using human primary hepatocytes and regular 2D cell culture.
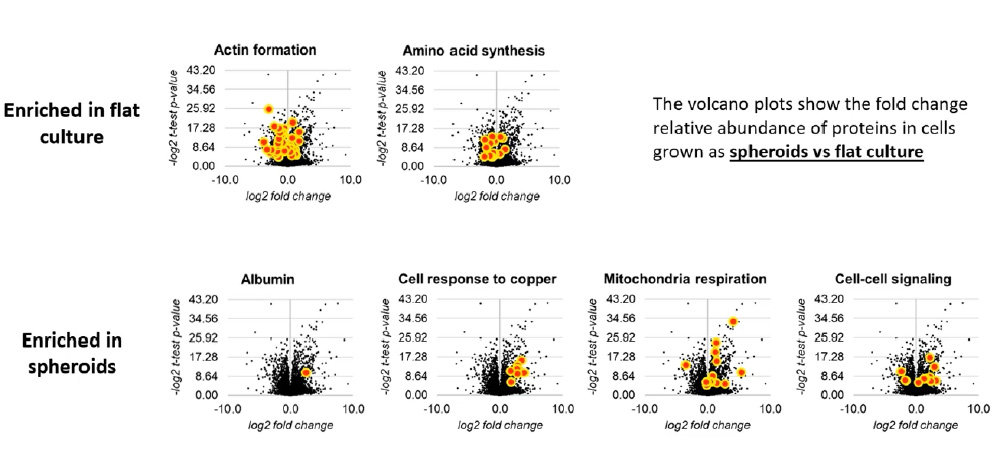
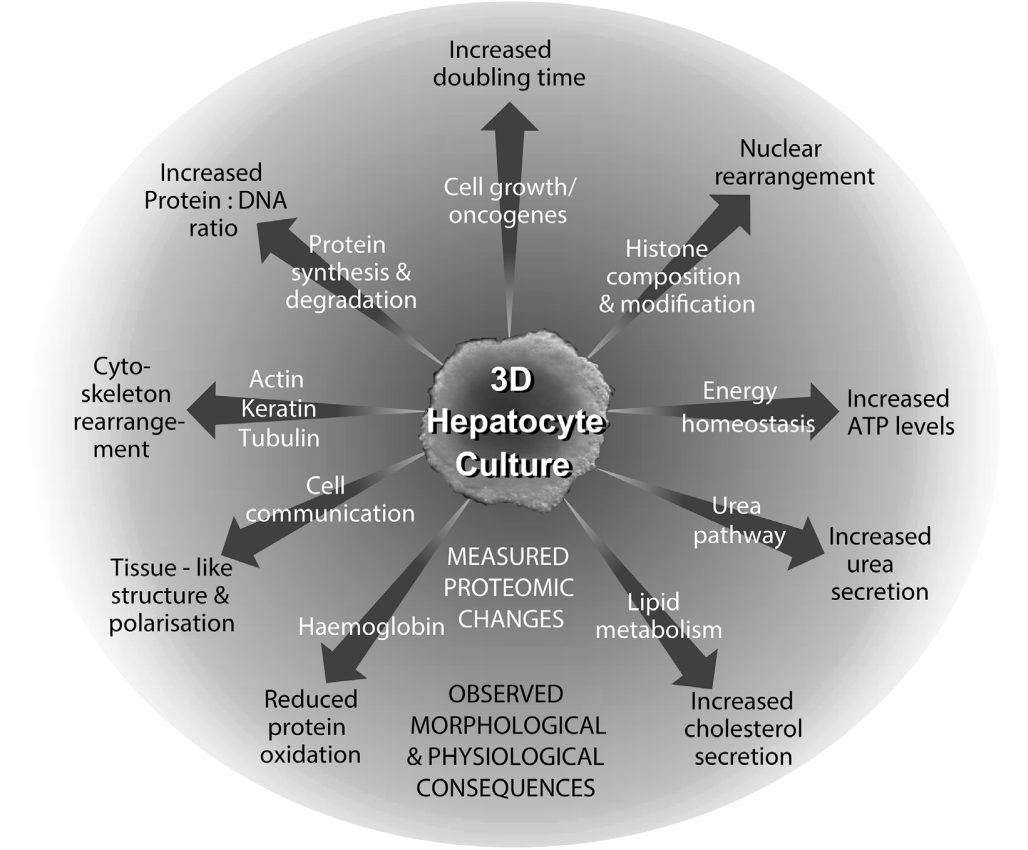
Proteomic changes
When comparing 2D and 3D cultured cells there are numerous changes thoughout the proteome.
Metabolic reprogramming
There are significant changes throughout the cells when cultured in 3D, which effects almost every aspect of cellular metabolism. These changes are the foundation for profound differences in architechture, functionality and physiology.
Epigenetics
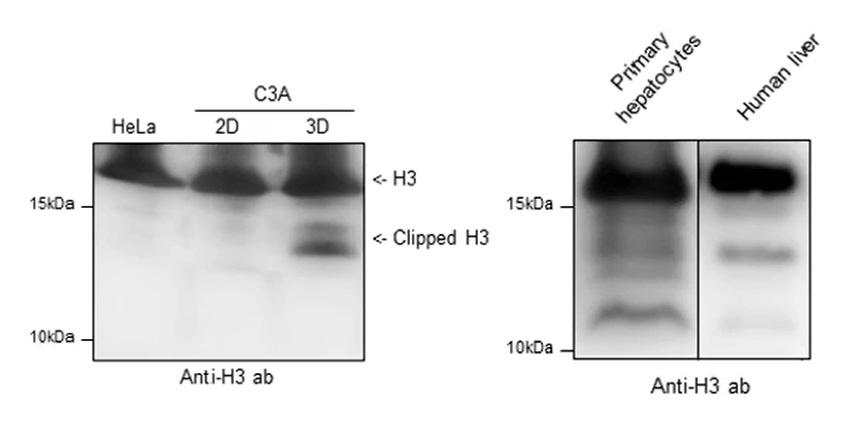
Spheroids dipaly histone marks and clipping not seen in a 2D flat culture. Histone clipping is associated with altered geneexpression.